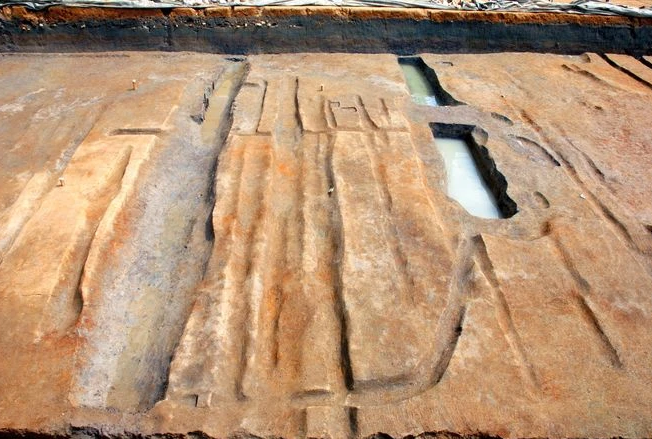
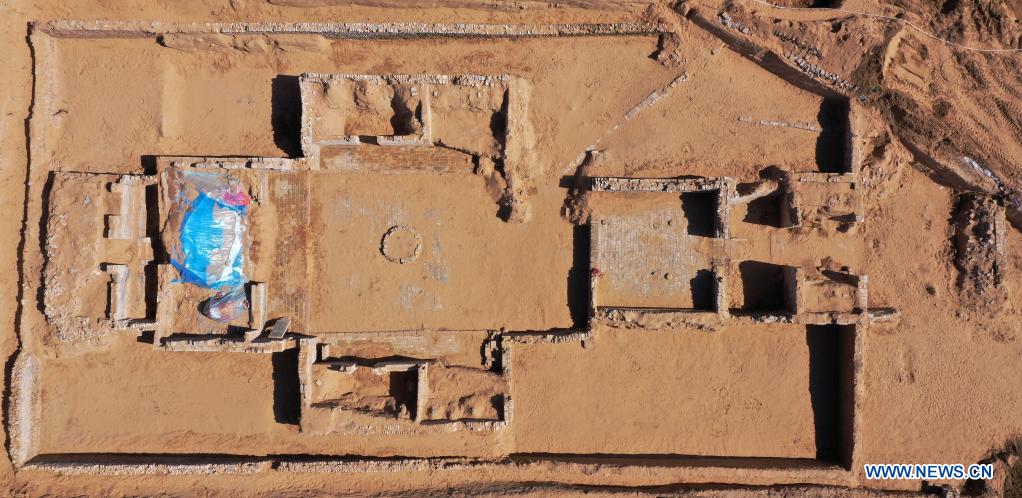
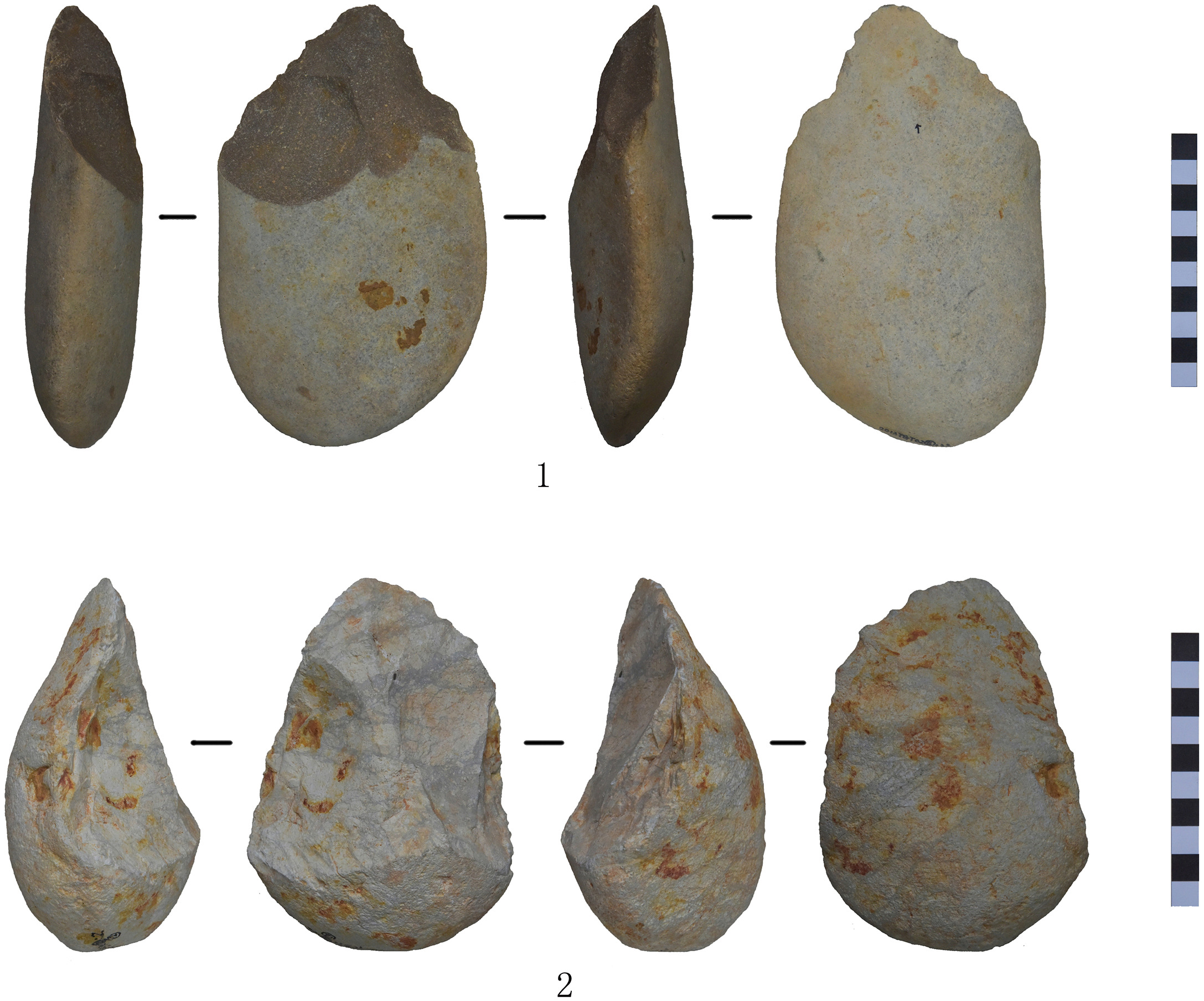
New fieldwork or research discoveries? Upcoming conference or workshop? New job opening or fellowship posting? New book?
Share the latest news of your work with your colleagues, advertise for job or fellowship openings, find participants for your conference session and more on the SEAA blog.
Guidelines: All posts should be related in some way to East Asian Archaeology. When writing your post, please use capital letters for surnames. Original script (Chinese, Korean, Japanese) for East Asian place names, personal names, or archaeological terms is encouraged. For the transcription of East Asian language terms, Pinyin for Chinese, Hepburn for Japanese, and the Korean Government System (2000) for Korean is encouraged.
Contributions should be limited to around 500 words and 1-2 images. For longer descriptions of your projects, you may consider the Reports section of the Bulletin (BSEAA).
Members can submit their news posts to the SEAA web editor via the website (see SEAA Members' Area for details and instructions on blog submissions) or via email. Non-member contributions are also welcome and may be submitted via email to the SEAA web editor.
The editor(s) reserves the right to carry out minor editing, or to decline contributions inappropriate to the objectives of SEAA.